latest articles
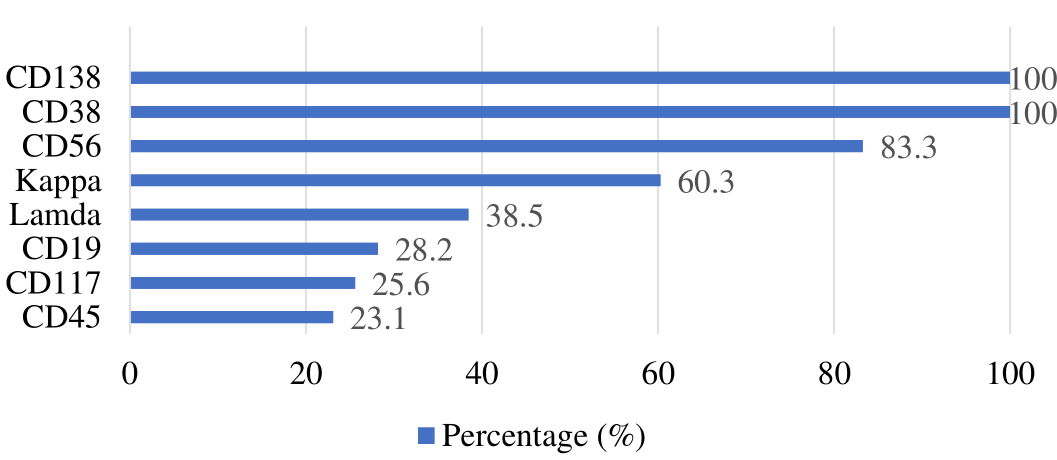
Immunophenotypic Expression and its Association with Prognostic Factors, Clinical Stages, and Clinical Profiles in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Plasma Cell Myeloma: Insights from Two Tertiary Care Centers
by Ismail
N.,
Pei Chi
L.,
Nik Yusoff
N., R., M.,
Mohamed
R.,
Hamzah
R.,
Farid Johan
M.,
Hassan
R.,
Mohamed Yusoff
S.
Summary: Plasma cell myeloma (PCM) is an incurable clonal neoplasm of plasma cells, which typically presents a poor prognosis. This study aimed to determine the clinical profile of newly diagnosed plasma cell myeloma cases in two tertiary care centers in Malaysia and evaluate the association of aberrant immunophenotypic expression with prognostic factors and clinical stages.
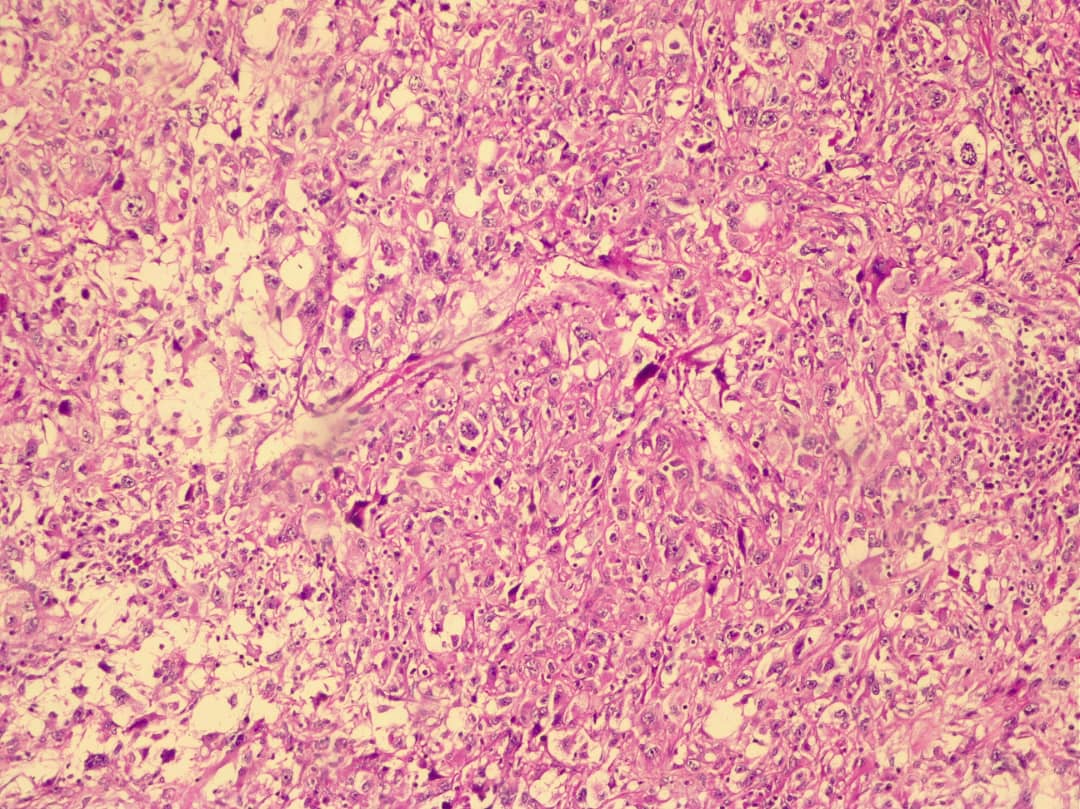
Sarcomatoid Renal Cell Carcinoma: Report of a Large Malignant Tumor with a Review of the Literature
by Naghibzadeh
Y.,
Javadizadeh
A.,
Amirian
F.,
Ramezani
M.
Summary: Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive kidney tumor with poor prognosis and distinct microscopic features. Traditional modalities versus new targeted therapy are used in different patients with controversial but some promising results.
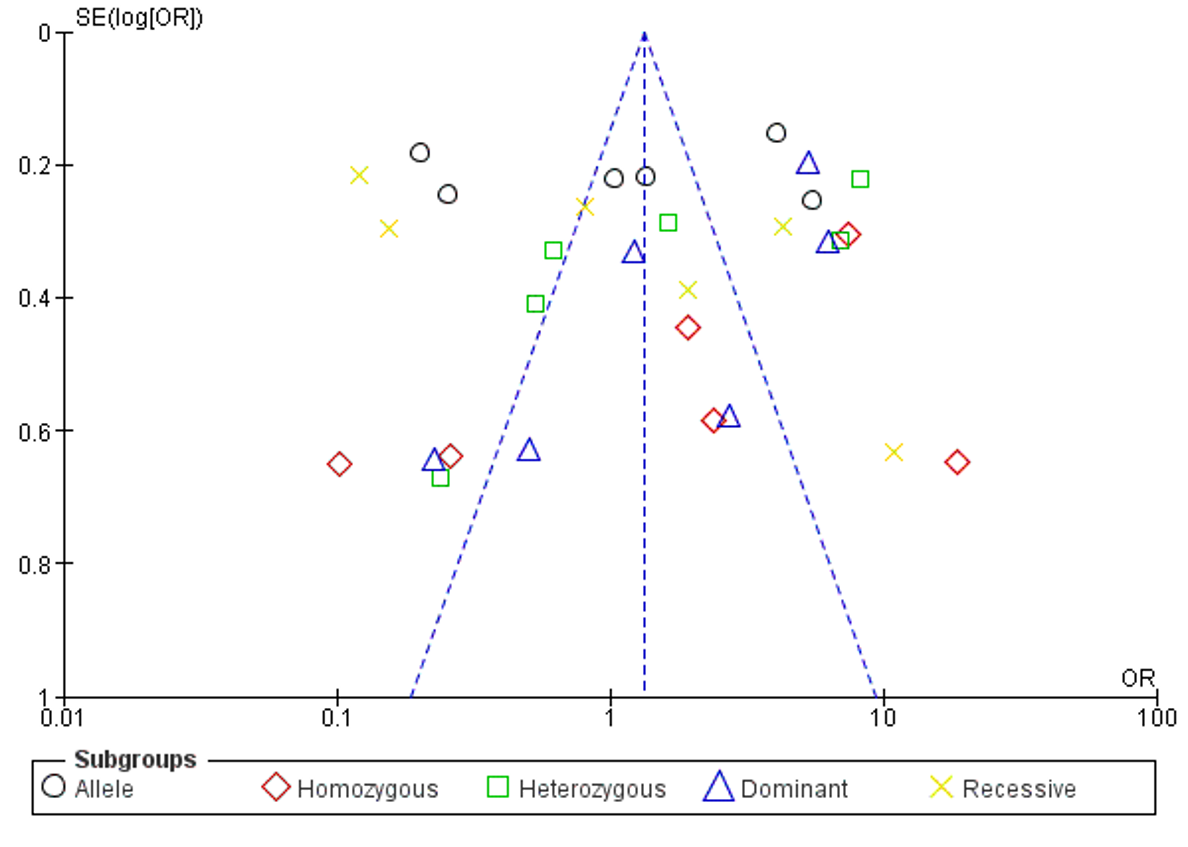
Genetic predisposition of interleukin-6 (rs1800797) polymorphism in cervical cancer: A Meta-analysis
by Prema
A.,
Kalarani
I.,
Veerabathiran
R.
Summary: Cervical cancer is a significant health burden, especially in less developed countries with limited access to HPV vaccines and screening. Dysregulation of immune cells, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and proinflammatory mediators have been implicated in cancer progression. SNPs in the IL-6 gene are thought to influence cervical cancer. A meta-analysis investigated the relationship between the IL-6 rs1800797 polymorphism and cervical cancer risk.
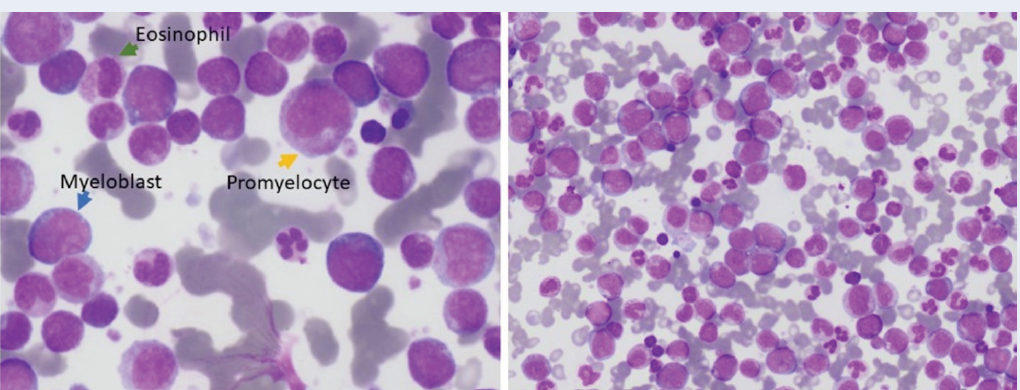
An Uncommon Presentation of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Osteolytic Bone Lesion as the Initial Manifestation
by Zulkeflee
R., H.,
Hassan
M., N.,
Zulkafli
Z.,
Noor
N.,
Husin
A.,
Abdullah
A., D.,
Yusoff
S., M.,
Ramli
M.,
Bahar
R.,
Rahman
W., S., W., A.,
Zawawi
N.
Summary: Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative neoplasm that typically occurs in the fifth and sixth decades of life with presentations usually confined to hematopoietic tissues—primarily blood, bone marrow, and spleen. However, primary presentation of CML as extramedullary involvement (osteolytic lesion) is extremely rare, occurring in less than 1% of cases.
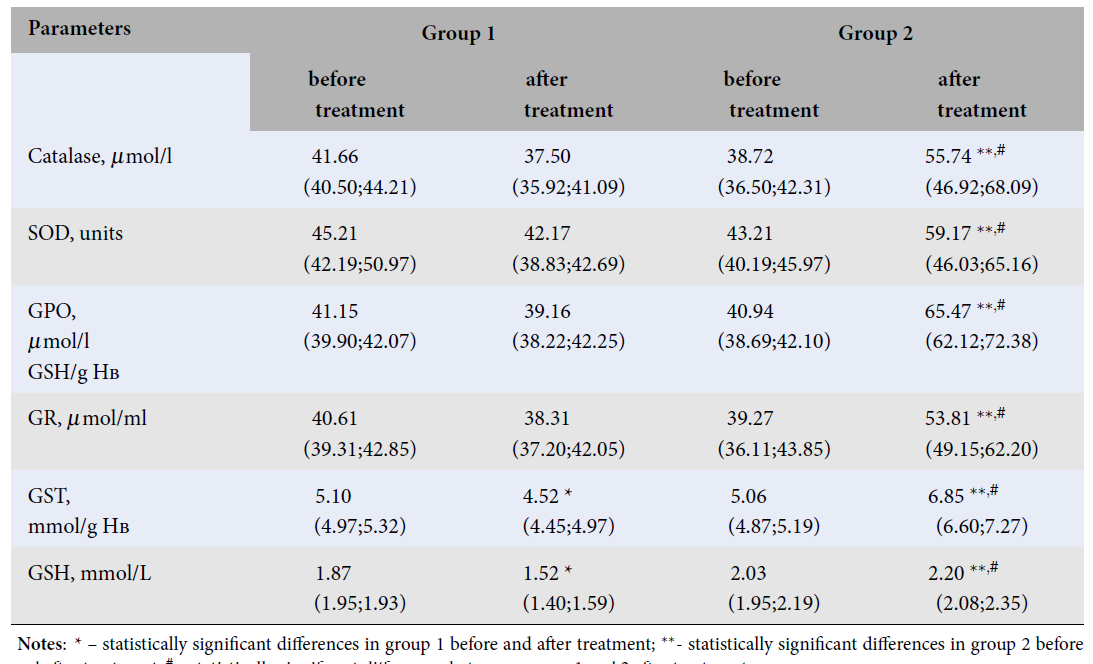
Impact of Antioxidant Therapy on Lipid Peroxidation and Venous Hemodynamics in Women with Pelvic Venous Incompetence
by Darenskaya
M.,
Stupin
D.,
Semendyaev
A.,
Kolesnikov
S.,
Tukhieva
D.,
Kolesnikova
L.
Summary: Pelvic varicosity, a subset of pelvic venous incompetence (PVI), is considered a multifactorial, chronic disease with a progressive course. One effective therapeutic approach may be the use of drugs that inhibit oxidative stress (OS) reactions. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of an antioxidant complex on the state of the lipid peroxidation system and venous hemodynamic parameters in the treatment of patients with pelvic varicose veins.
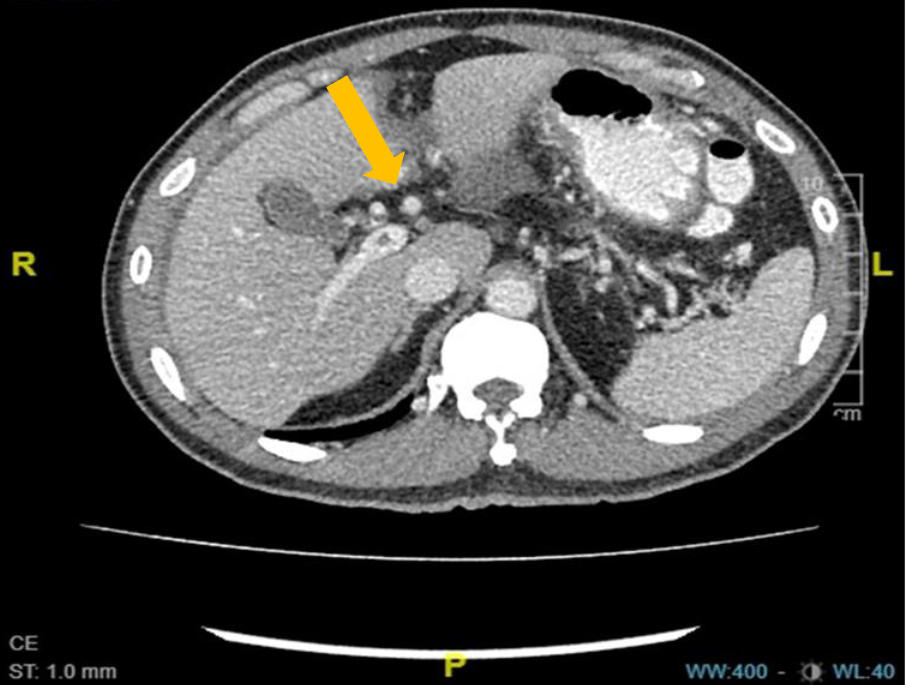
Antithrombin deficiency with portal vein and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis—a case report
by Saidin
N., I., S.,
Jamallodin
F., B.,
Hassan
M., N.,
Iberahim
S.,
Abdullah
A., H.,
Zahidin
M., A.,
Zulkafli
Z.,
Noor
N. H. M.
Summary: A deficiency in antithrombin (AT) can be hereditary or acquired. It is characterized by an AT activity level that is less than 80% of normal or the lower limit of the reference range on a regular basis. In some cases, AT deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of thromboembolism.
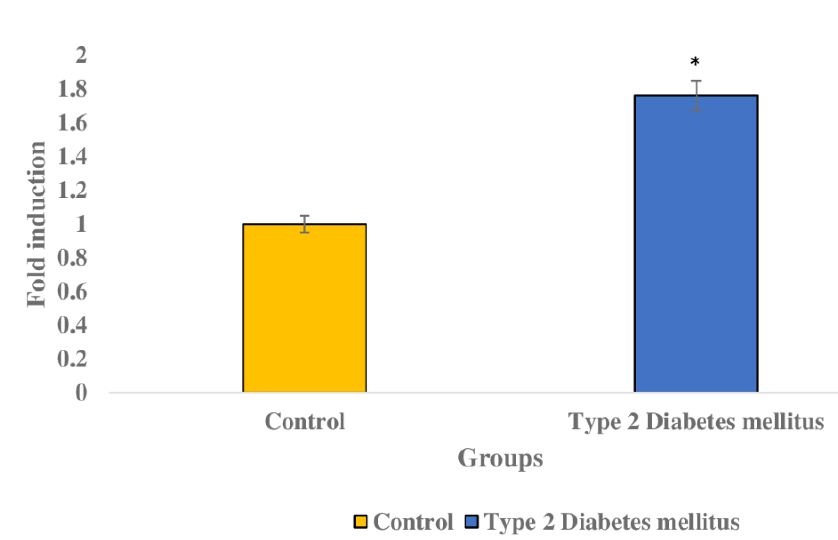
microRNA-9-5p and its target nuclear factor kappa B are differentially expressed in type-2 diabetes patients
by Narayan
R., N.,
Kizhakke Parambath
A.,
Puthiya Purayil
A., S.,
Sekar
D.
Summary: According to various studies, type II diabetes (T2D), a serious metabolic disease marked by insulin resistance with disrupted glucose homeostasis, affects millions of people worldwide and may reach 552 million cases by 2030. Recent studies highlighted the key role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in various cellular processes related to disease development. Moreover, studies have indicated increased concentrations of miR-9-5p in T2D individuals, thereby suggesting a possible role for miR-9-5p in influencing the regulation of glucose metabolism. Hence, the current study aims to focus on miR-9-5p and its target nuclear factor kappa B (NFkB1) in T2D by utilizing publicly available genome sequences to point out their potential as diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers.
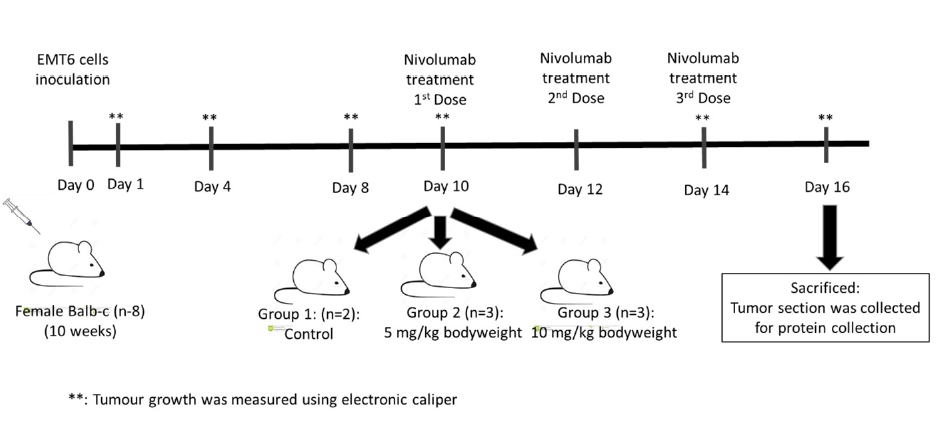
Different concentrations of nivolumab reduce PD-1 expression but not tumour growth in an EMT6 mouse model
by Sham
N., F., R.,
Hasbullah
H., H.,
Hasani
N., A., H.,
Hasan
N.,
Othman
S.,
Osman
N., J.,
Karim
M., K., A.,
Fuad
S., B., S., A.,
Ibahim
M. J.
Summary: The interaction between the T cell immune checkpoint proteins, the programmed death-1 (PD-1) receptor, and its ligand PD-L1 plays a crucial role in T cell suppression and the evasion of cancer cells from immune detection, thereby promoting tumour growth. Nivolumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, disrupts this interaction, offering a potential therapeutic anti-cancer strategy. The goals of this study were to identify the optimal dosage of nivolumab that effectively decreases PD-1 protein expression in a mouse model, and to examine the impact on tumour growth.
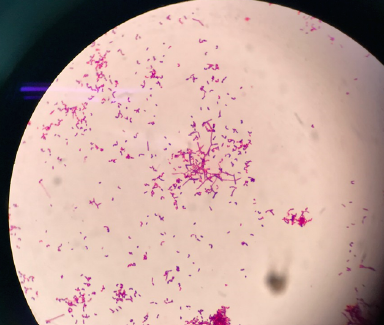
A case report of corneal abscess caused by Nocardia farcinica
by Mai
L.,
Tho
V., N., A.,
Van
D., T., T.,
Phu
T. T.
Summary: Keratitis caused by Nocardia, a Gram-positive bacterium prevalent in soil, is an infrequent ocular infection typically following corneal trauma or exposure to soil or vegetation. Nocardia farcinica, in particular, is an exceedingly rare causative agent of keratitis, with few documented cases worldwide and none previously reported in Vietnam.
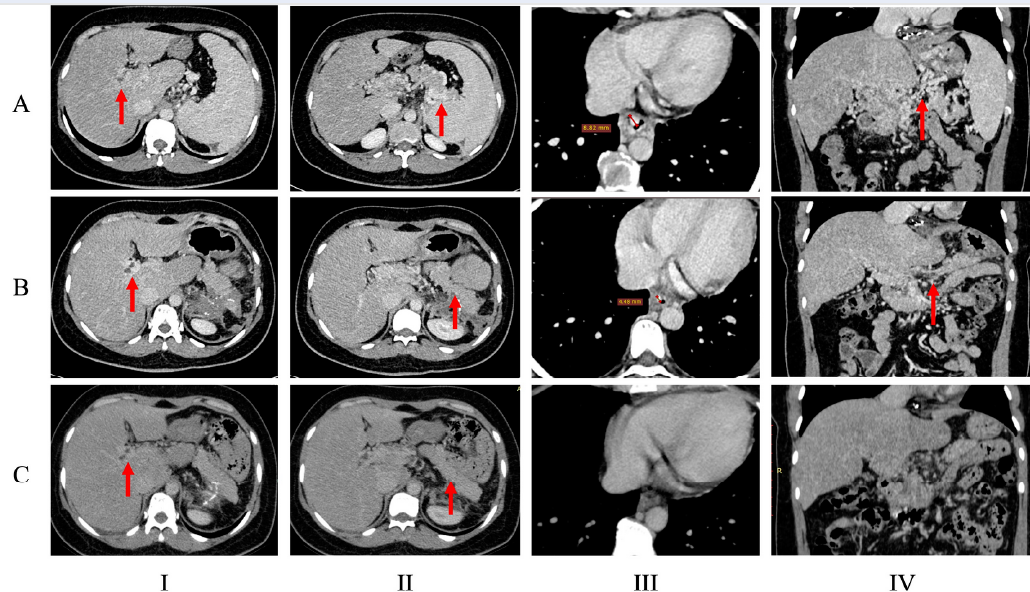
First report of chronic portal vein thrombosis successfully managed with splenectomy and long-term direct oral anticoagulants
by Huynh
T., M.,
Nguyen
S., T.,
Lam
N., T.,
Pham
A., L.,
Nguyen
S. V.
Summary: We report a rare case of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) secondary to idiopathic hypercoagulability leading to non-cirrhotic portal hypertension and cavernous transformation. The patient had a history of acute PVT and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis, which was initially managed successfully with anticoagulation therapy. However, the discontinuation of treatment precipitated a transition to chronic PVT and subsequent cavernous transformation. This condition manifested clinically as esophageal and gastric varices, posing a significant bleeding risk. Attempts to mitigate portal hypertension through medical management and endoscopic interventions had limited success. The anatomical complexities presented an insurmountable challenge to transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement, and thus alternative treatment strategies were considered. A splenectomy markedly improved the patient's condition. Over a 2-year follow-up period, with the aid of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), the patient remained stable; further endoscopic procedures were not required, and the patient did not experience a recurrence of thromboembolic or hemorrhagic events. This case underscores the complexity of PVT management and highlights the need for individualized treatment approaches in the face of anatomical and therapeutic challenges.
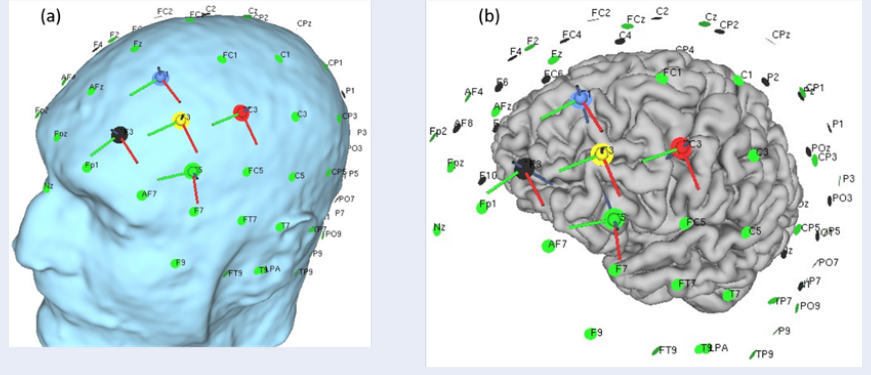
Polarity-specific changes in the E-field and focality in mild cognitive impairment patients for HD-tDCS and reverse HD-tDCS
by Pancholi
U.,
Dave
V.
Summary: This study analyzed polarity-specific changes in the electric field (E-field) and the focal point of tDCS stimulation for both High-Definition tDCS (HD-tDCS) and reverse HD-tDCS considering the head geometry of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) patients. The distance between the left preauricular (LPA) and right preauricular points as well as the inion and nasion were calculated in 3D to measure correlations.
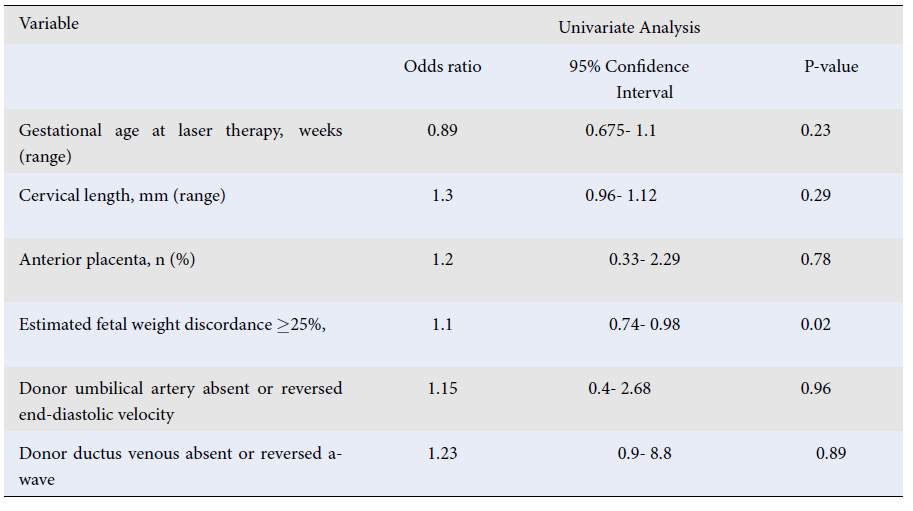
Evaluation of the success of fetoscopic laser coagulation in placental vascular anastomoses and the role of fetal vascular Doppler before laser treatment in twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
by Marsoosi
V.,
Mansouri
N.,
Azizi
A.,
Eslamian
L.,
Jamal
A.,
Naemi
M.,
Nurzade
M.,
Ariana
S.,
Sadeghi
M.
Summary: Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a critical prenatal complication in monochorionic diamniotic twins with a high risk of mortality and neurological sequelae if left untreated. Of the various therapeutic approaches, fetoscopic laser surgery (FLS) has emerged as the predominant treatment modality worldwide. This study evaluates the outcomes and preoperative risks of TTTS treatment via FLS.
Immunoinformatics approach to Rift Valley fever virus vaccine design in ruminants
by Oladipo
E., K.,
Taiwo
O., R.,
Teniola
F., O.,
Temitope
A., P.,
Boluwatife
A., M.,
Oluwaseyi
O., I.,
Oladimeji
B., V.,
Taiwo
J., I.,
Adejumo
I. O.
Summary: Rift Valley fever (RVF) represents a significant public health challenge and economic burden due to its impact on livestock and potential to affect humans. Despite attempts to develop vaccines against the Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV), existing options are limited by concerns regarding the inability to differentiate between vaccinated and infected animals, vaccine-associated viremia, and the need for booster doses. This underscores the urgent need for a novel, effective, and safe vaccine, especially for use in ruminants, which this study seeks to address.
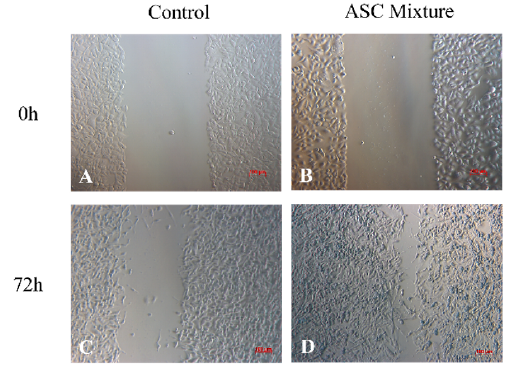
A mixture of secretions and extractions derived from antler stem cells heal open wounds in rats with a tendency to leave no scar
by Huynh
P.,
Cao
A.,
Le
T.,
Nguyen
S.,
Vu
N.
Summary: Deer antlers are remarkable organs as they can regenerate seasonally and leave no scars. Antler-derived stem cell therapy applications are of increasing interest in food, beauty, and medicine.
Journal Collections

Covid-19 publications
Journal Supplements
Conference Abstracts
Journal Collections

Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine
Special Issues
Special Issues
Journal Collections

Natural Extract
Publication Awards

The best original research articles
Editors' quote

Phuc Van Pham, Editor-in-Chief
Affiliation

Why publish with Biomedical Research and Therapy



 Biomedpress
Biomedpress





