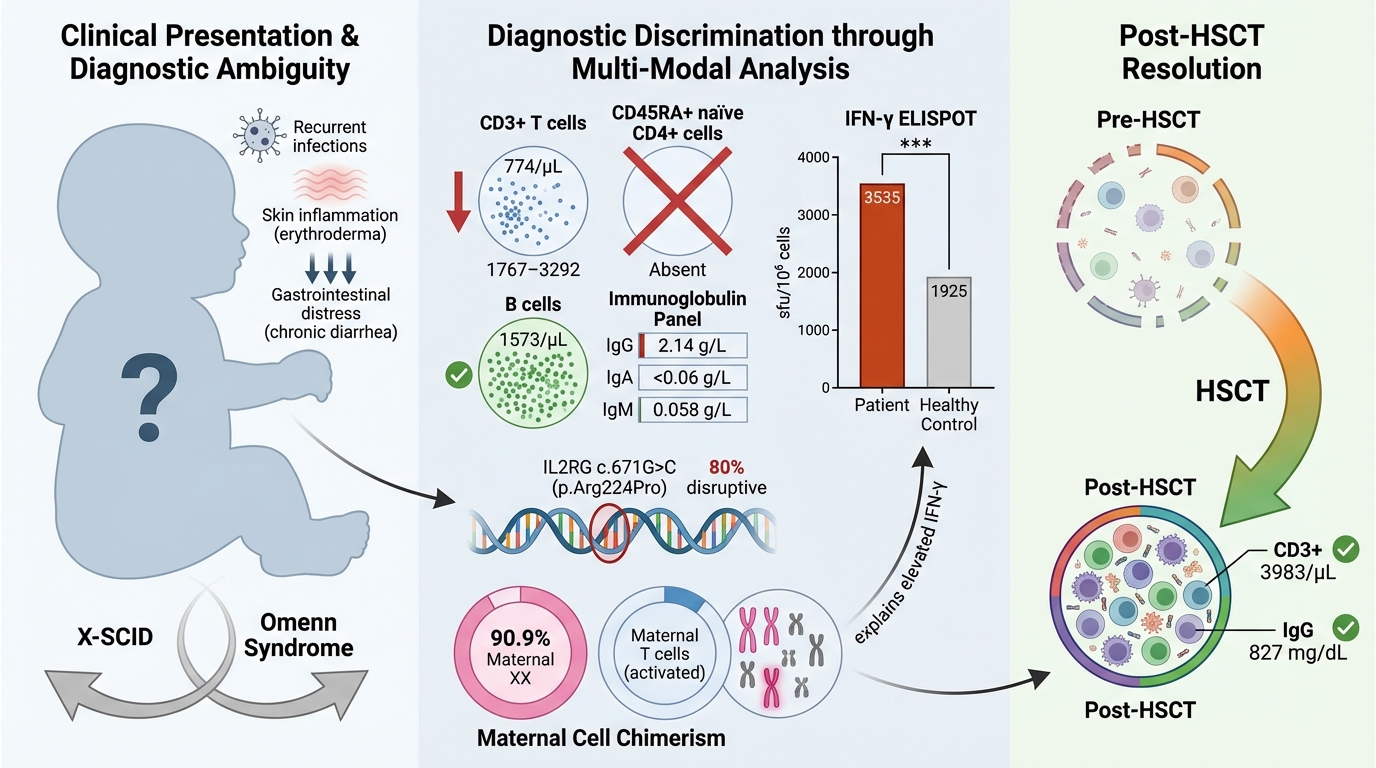
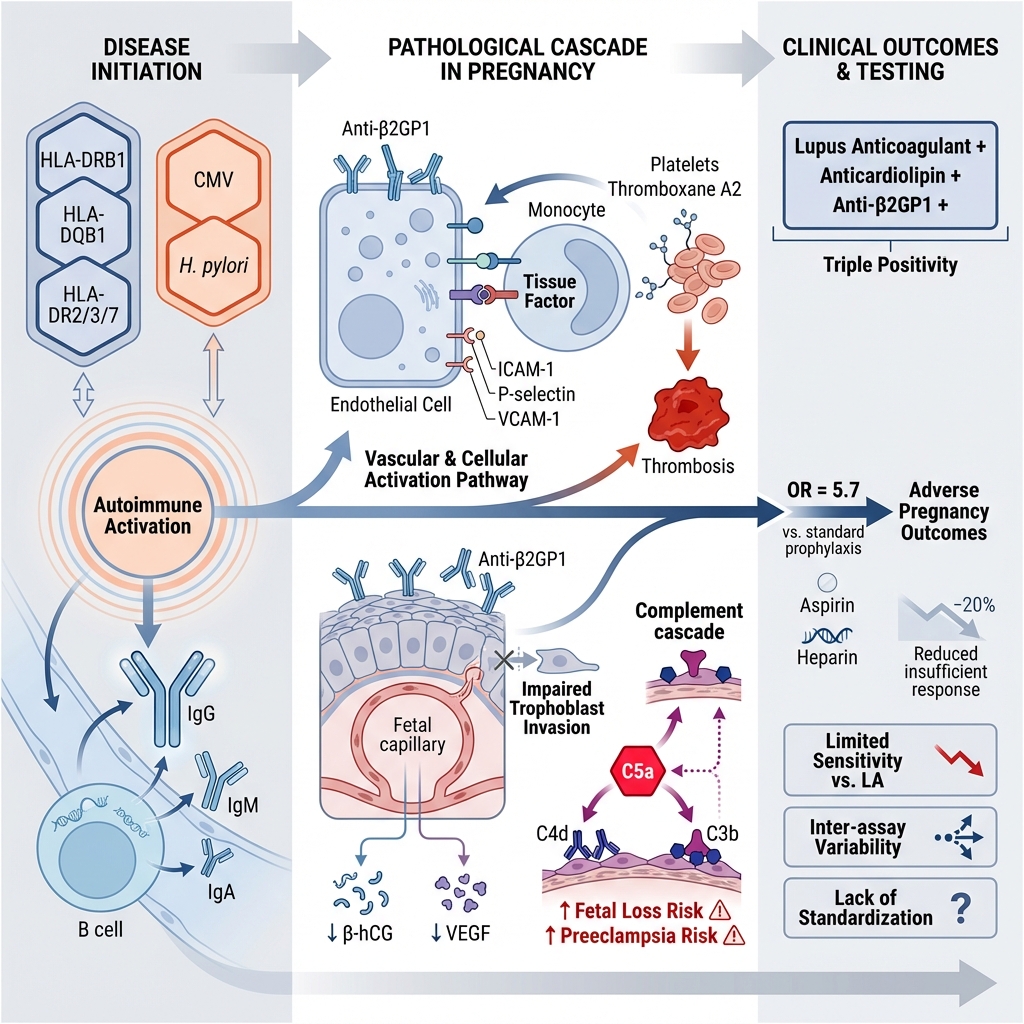
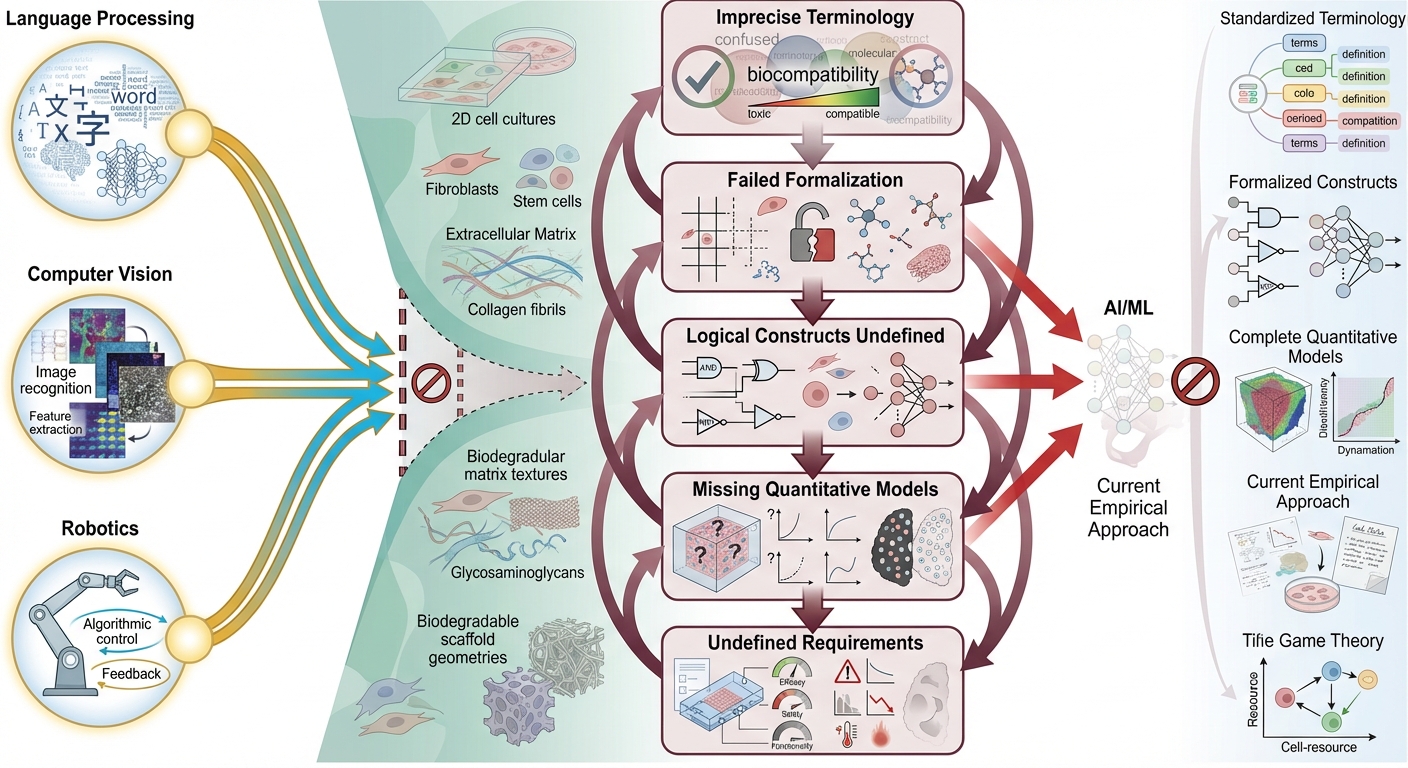
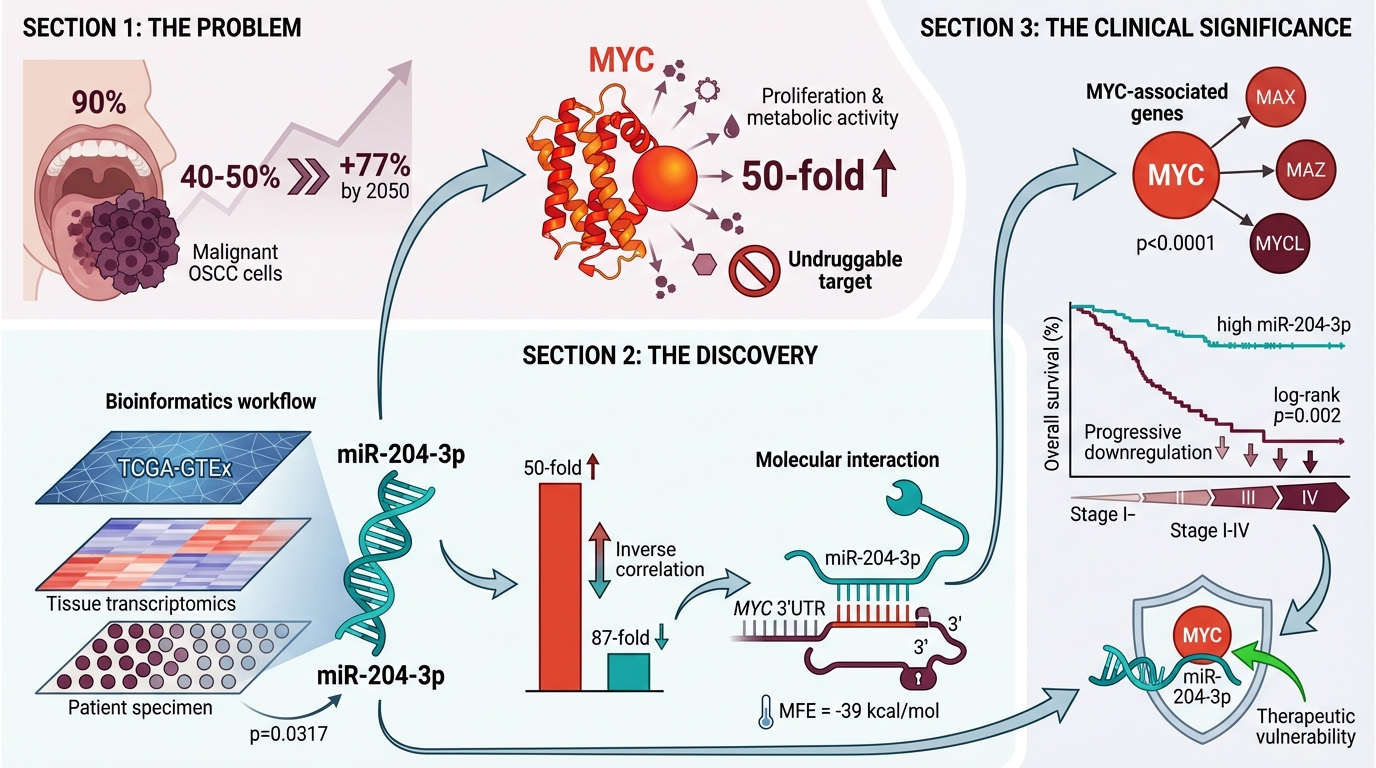
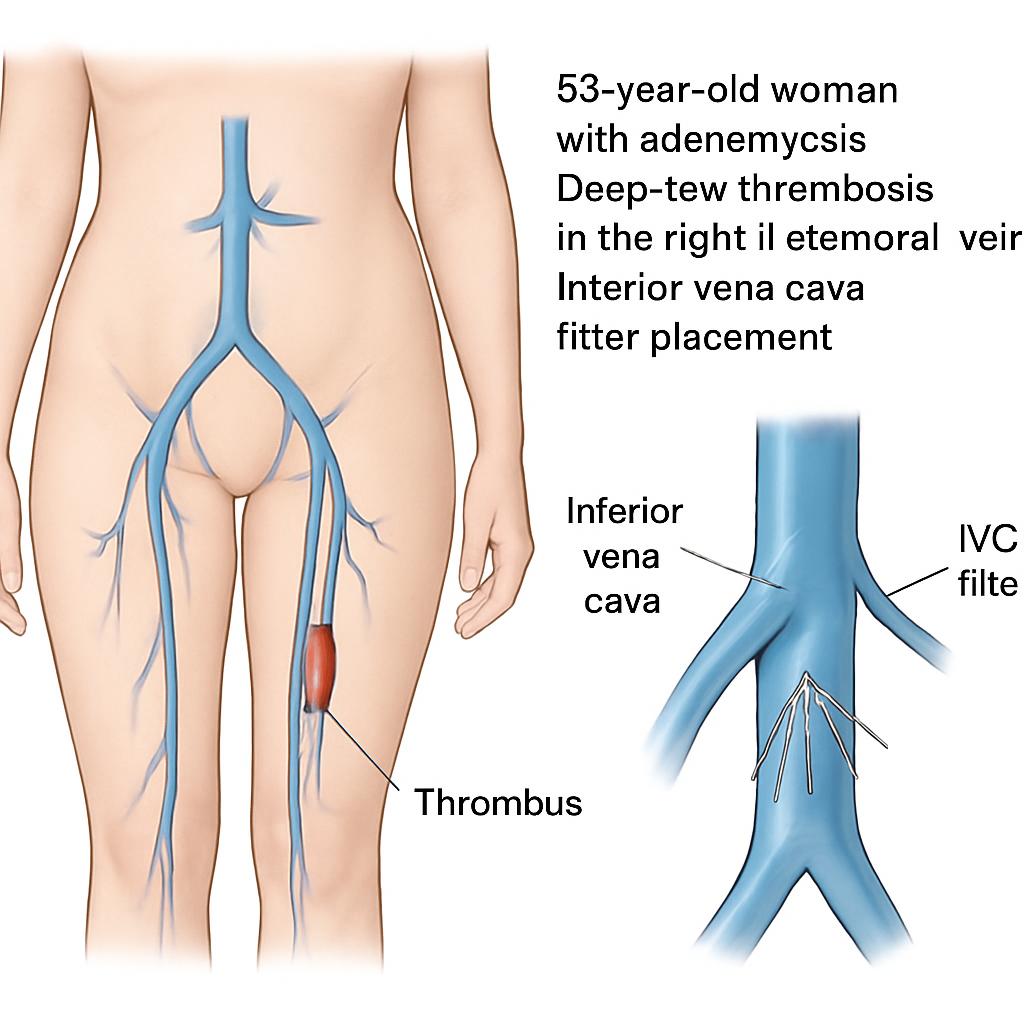
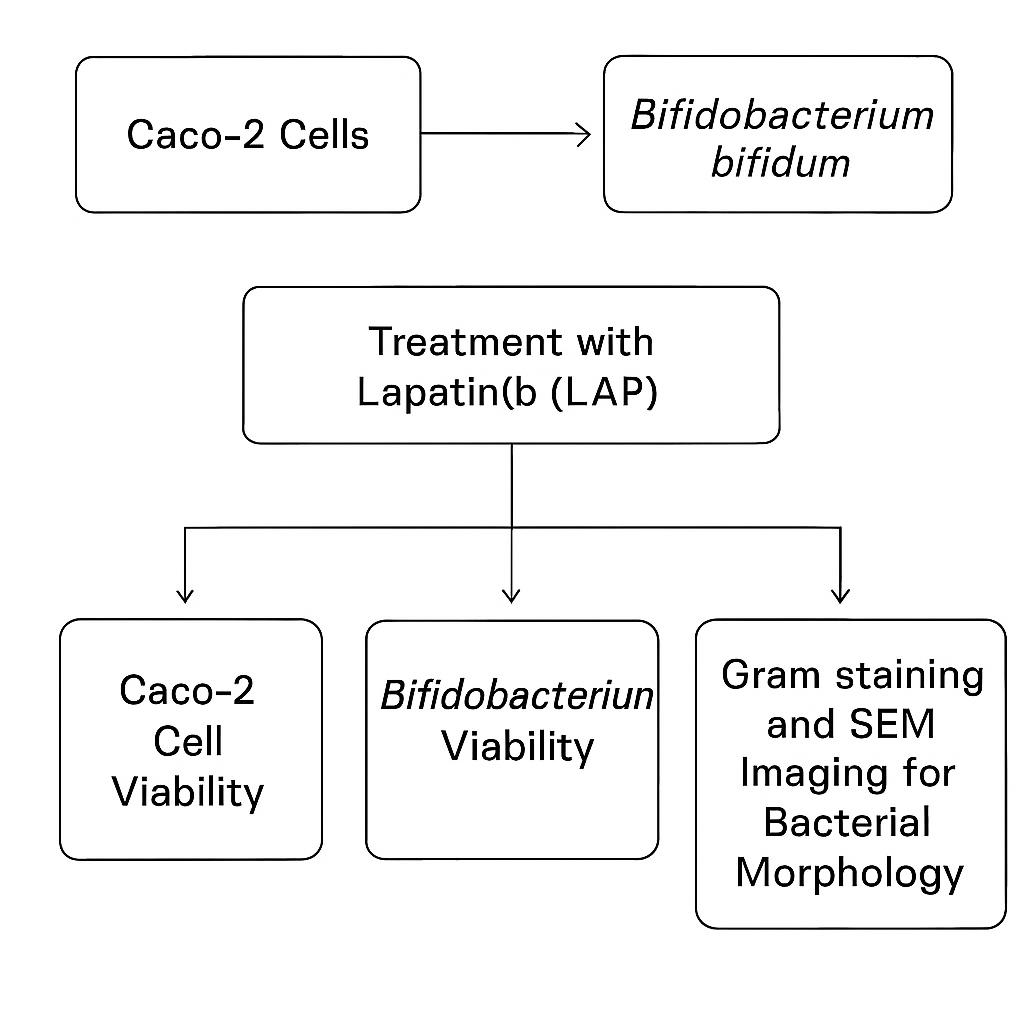
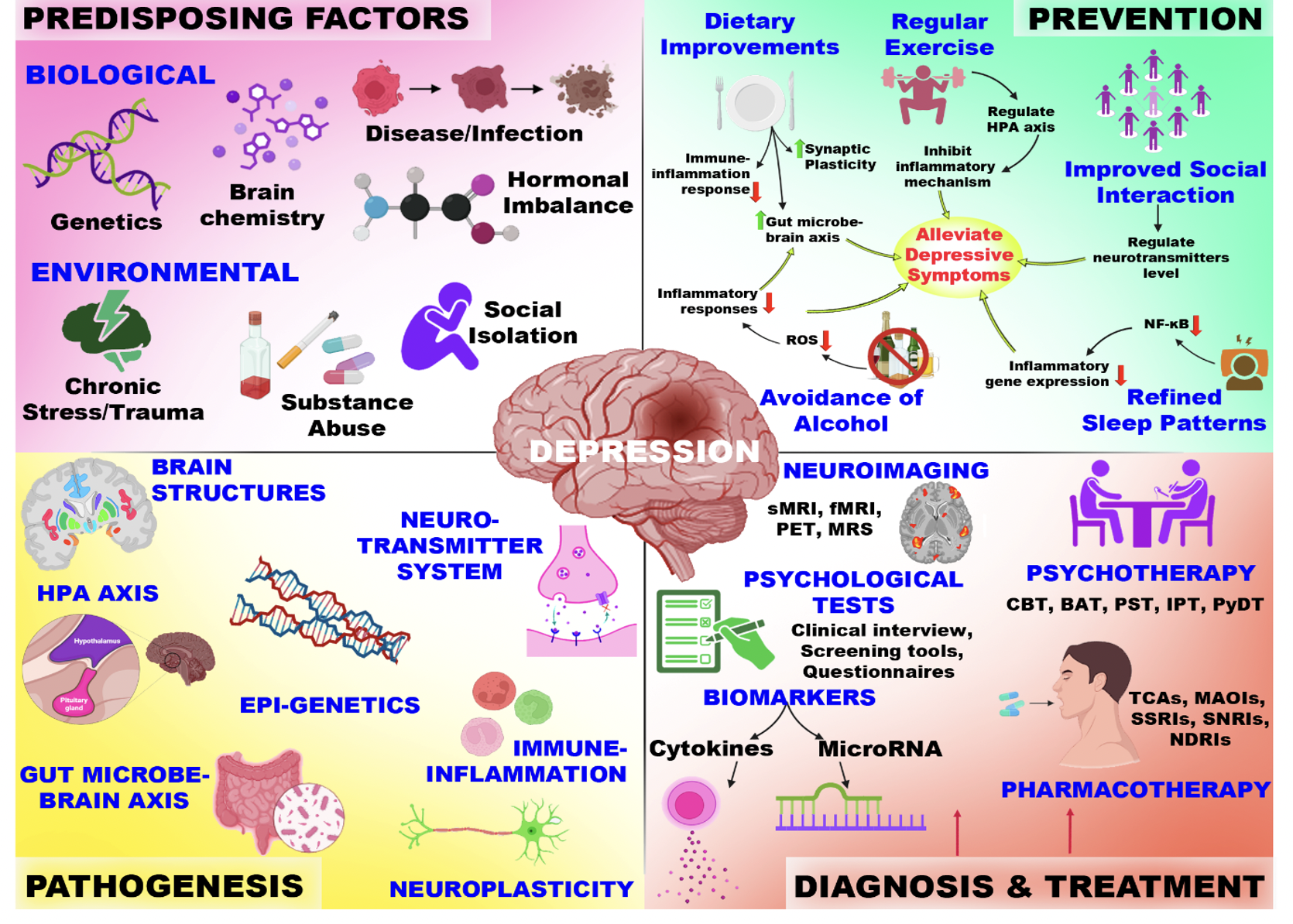
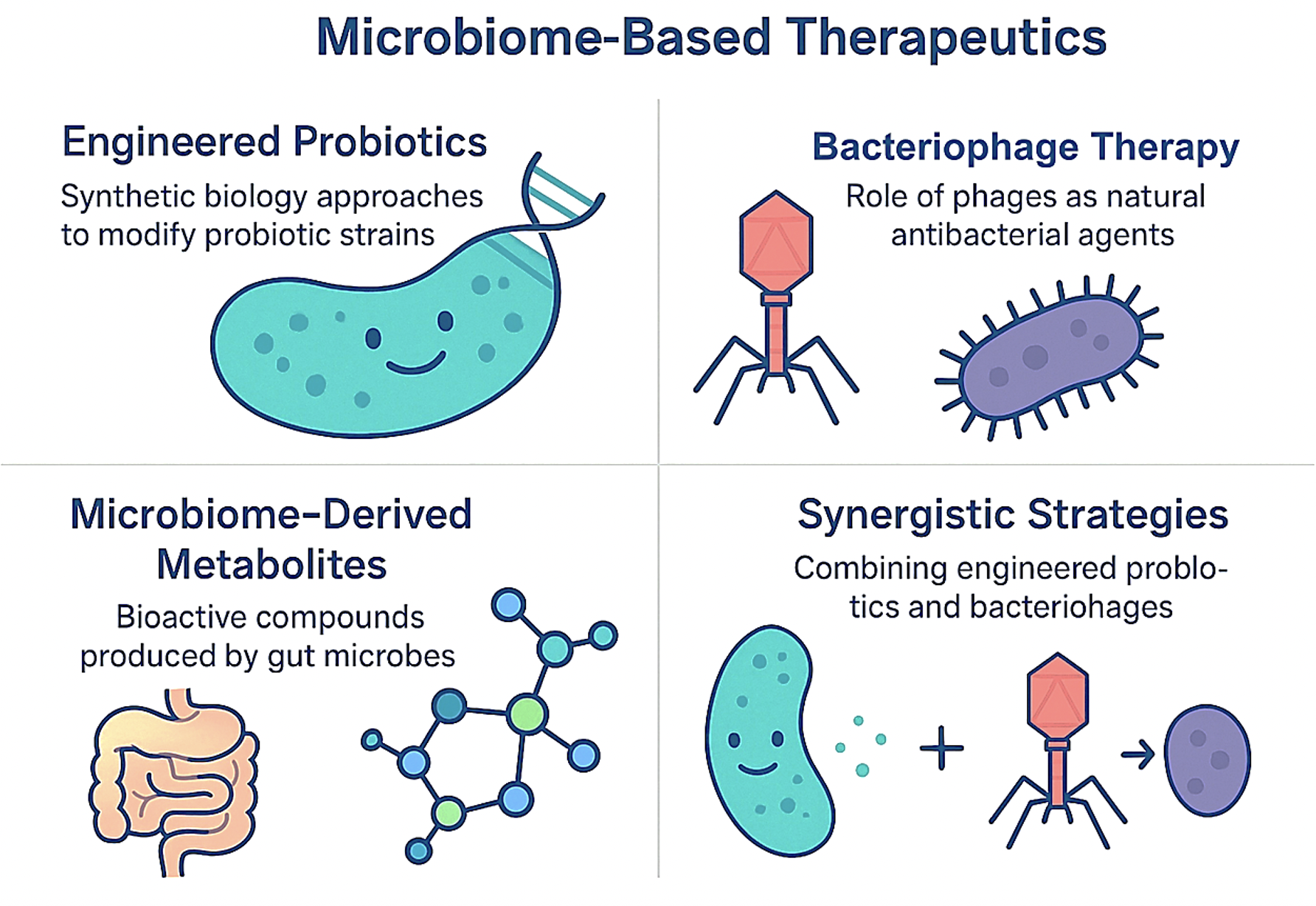
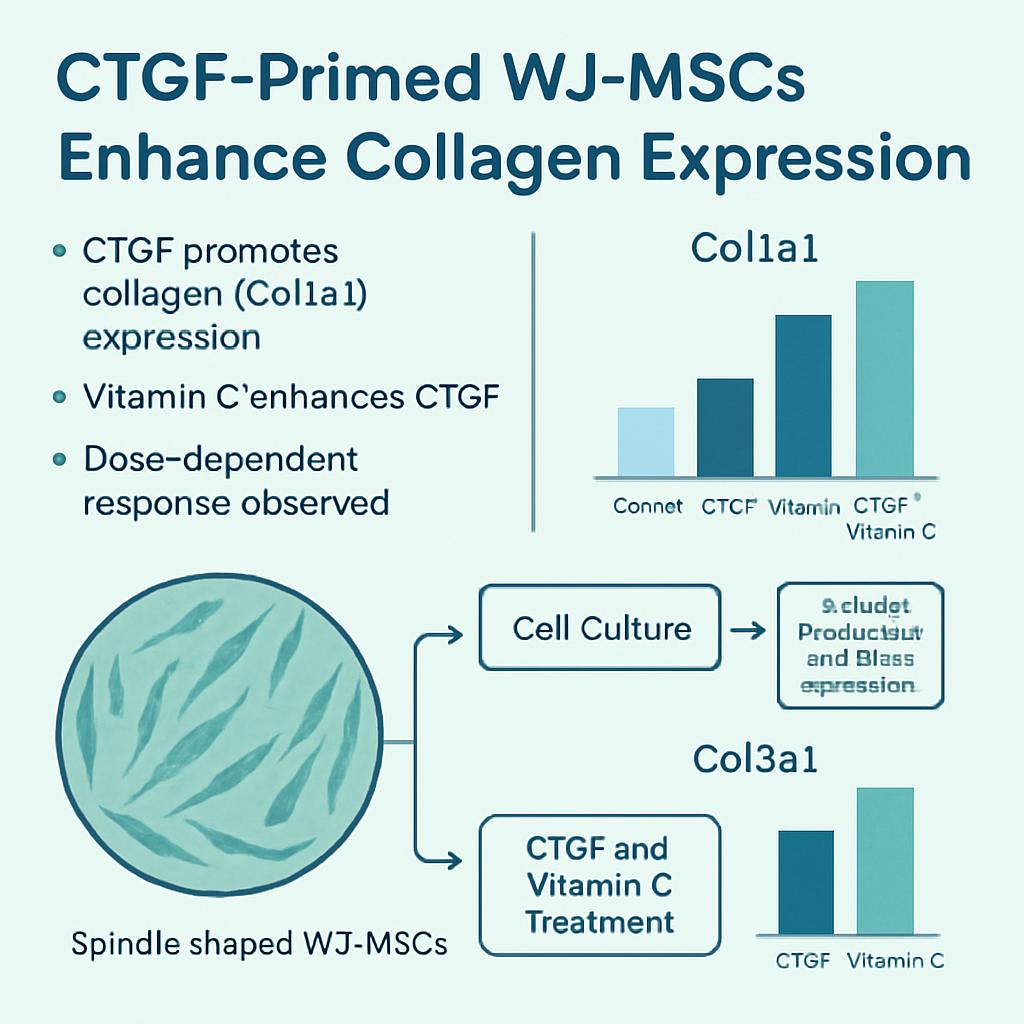
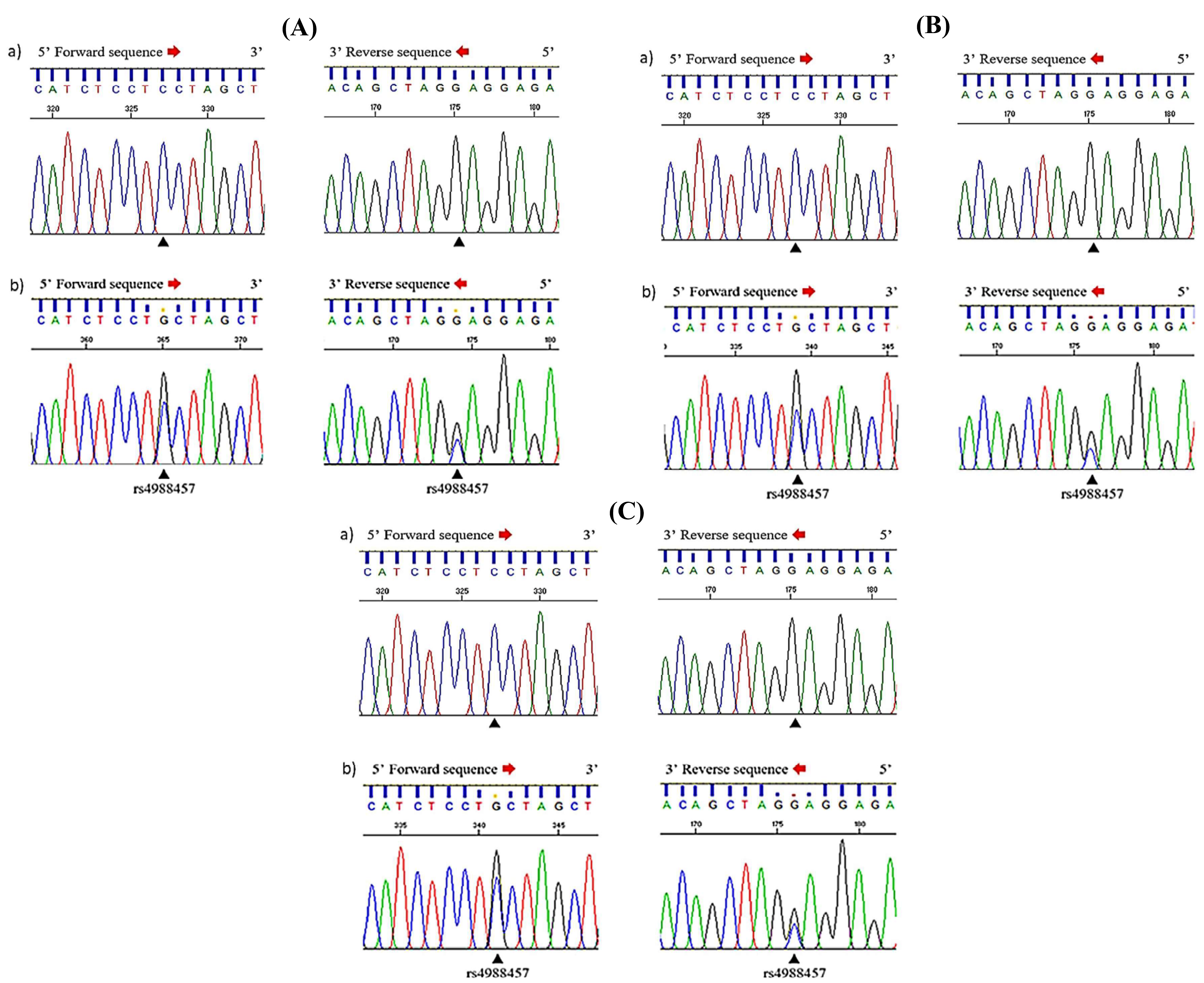
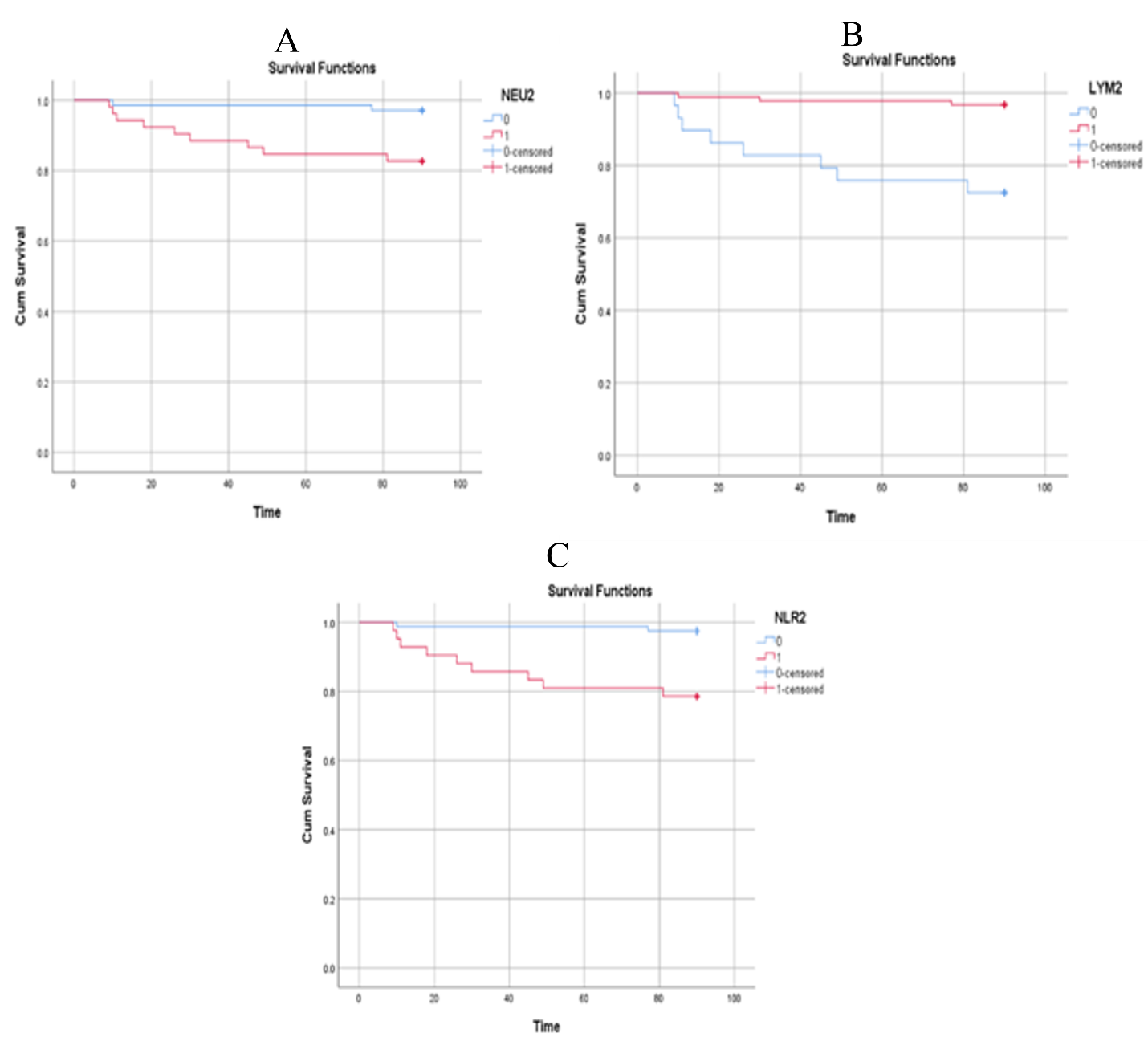
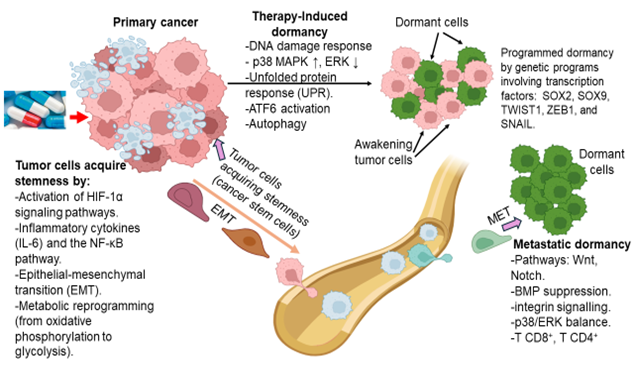
Phuc Van Pham, VNUHCM-US Stem Cell Institute, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
Important Announcement Regarding Language Editing for Manuscripts from Non-Native English Speakers
To ensure the highest standards of clarity and scientific communication in all published works, Biomedpress is implementing a new policy for manuscripts submitted by non-native speakers of English.
We are committed to cooperating with authors with the right attitude and approach to successfully complete the final publication of their manuscripts. However, quality control of a manuscript’s language is non-negotiable for Biomedpress and all its journals. The language of a manuscript must meet the rigorous requirements of international academic publishing.
Effective immediately, for manuscripts submitted by non-native speakers of English, authors will be required to provide a Language Editing Certificate during the revision process. This certificate must be provided by a reputable native English language editing company or a native English-speaking biomedical scholar. It must verify that the manuscript's language has been professionally polished and meets a high standard of quality (Grade A).